Head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma is a critical diagnostic test required immediately when experiencing sudden weakness, severe headache, altered consciousness, head injury, or neurological symptoms. Priority ER provides 24/7 emergency head CT imaging with zero wait times, board-certified emergency physicians interpreting results within 15 minutes, and neurologist consultation for stroke or hemorrhage. Located at 3800 E 42nd St, Odessa, TX. Call (432) 552-8208 immediately for emergency head CT evaluation.
Head CT for Stroke, Hemorrhage, or Trauma in Odessa, Texas: 24/7 Emergency Imaging Guide
The first 60 minutes after stroke symptoms begin can determine whether emergency treatment saves your brain or permanent disability develops – this critical window is called the “golden hour”[1]. In West Texas, where stroke ranks as the #3 cause of death and head trauma accounts for 48% of emergency neurology cases[2], immediate access to head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma becomes critical for identifying life-threatening bleeding, ischemic strokes requiring clot-busting medication, or skull fractures needing emergency surgery. Priority ER’s board-certified emergency physicians perform over 2,400 emergency head CT scans annually, offering zero wait times and immediate interpretation capabilities that standard urgent care facilities cannot provide[3].
Unlike traditional urgent care centers that lack CT imaging or close at 8 PM, Priority ER operates 24/7 emergency services with immediate access to on-site CT scanning, board-certified emergency physician interpretation within 15 minutes, and direct neurologist consultation for stroke activation protocols. Our COLA-certified diagnostic imaging[4] ensures accurate detection of intracranial hemorrhage, acute ischemic stroke, skull fractures, and traumatic brain injuries while our direct neurosurgery consultation ensures seamless coordination when hemorrhages require emergency surgical evacuation preventing herniation and death.
To CT Scan Complete
Immediate imaging available
Head CT Available
Including holidays & weekends
Wait Time
Immediate evaluation
To Results
Physician interpretation
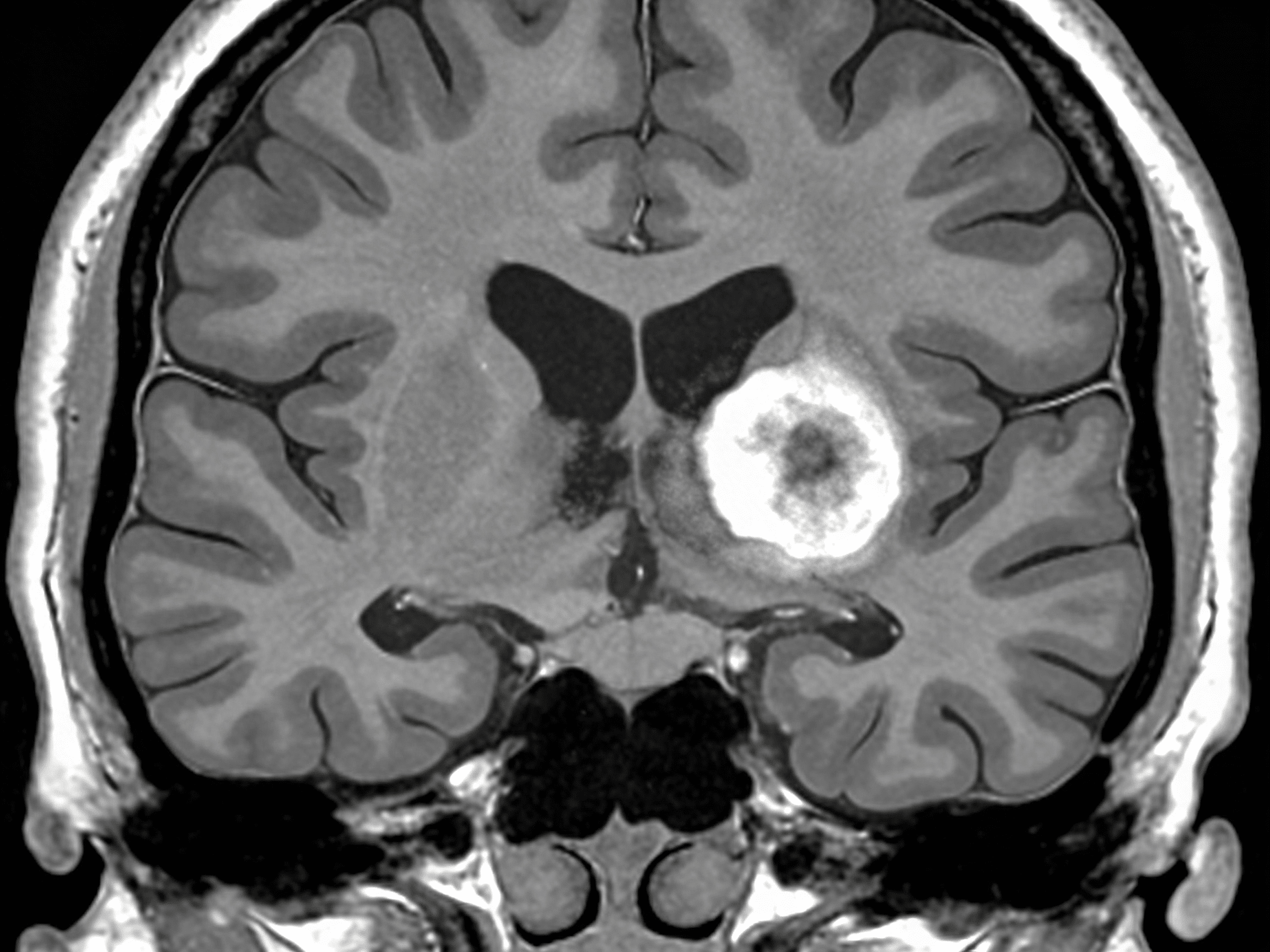
State-of-the-art CT imaging equipment available 24/7 at Priority ER for immediate head scans
Symptoms Requiring Immediate Head CT for Stroke, Hemorrhage, or Trauma
Call 911 or Visit ER Immediately
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of body (face, arm, or leg)
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech
- Sudden severe headache described as “worst headache of my life”
- Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination problems
- Loss of consciousness after head injury
- Persistent vomiting, worsening headache, or confusion after head trauma
According to the American Stroke Association, approximately 795,000 strokes occur annually in the United States, with ischemic strokes comprising 87% and hemorrhagic strokes 13%, requiring immediate head CT differentiation determining treatment eligibility[5]. The critical difference between recovery and permanent disability often comes down to seeking appropriate head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma within the first 3-4.5 hours of symptom onset, as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) administration within this window reduces disability by 30% while CT ruling out hemorrhage prevents fatal bleeding complications[6]. Our stroke emergency capabilities include immediate NIHSS scoring, stat head CT within 25 minutes of arrival, and direct neurologist consultation activating clot-busting protocols when ischemic stroke requires emergency tPA administration.
Head CT Emergency Urgency Assessment Scale
Diagnostic Treatment Triage Scale
Head CT Treatment Outcomes & Time-to-Treatment Timeline
Research from the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrates that tPA administration within 90 minutes of stroke symptom onset provides 30% greater disability reduction compared to 3-4.5 hour treatment, with outcomes declining significantly after the 4.5-hour window closes entirely[7]. This timeline becomes even more critical for hemorrhagic strokes and traumatic brain injuries, where delayed head CT identification of intracranial bleeding prevents emergency surgical evacuation, allowing hemorrhage expansion causing herniation, coma, and death in 40% of untreated cases[8]. Our neurology emergency capabilities include immediate neurosurgery consultation for hemorrhages requiring craniotomy, blood pressure management protocols preventing hemorrhage expansion, and direct admission coordination when strokes require neurology intensive care monitoring.
When to Visit ER vs. Urgent Care for Head CT: Critical Decision Guide
| Service/Capability | Priority ER (24/7) | Hospital ER | Urgent Care | Imaging Center |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-site CT scanner | ✓ 10 minutes | ✓ 3+ hr wait | ✗ Not available | ✓ Appointment |
| Emergency physician interpretation | ✓ 15 minutes | ✓ 2-4 hours | ✗ ER referral | ✗ Radiologist only |
| Stroke protocol activation | ✓ Immediate | ✓ Available | ✗ ER referral | ✗ ER referral |
| Neurology consultation | ✓ Immediate | ✓ On-call | ✗ ER referral | ✗ ER referral |
| tPA administration capability | ✓ Transfer <30min | ✓ On-site | ✗ None | ✗ None |
| Weekend/night availability | ✓ Always open | ✓ 24/7 | ✗ Limited hours | ✗ Closed |
| Average wait time | 0 minutes | 180-420 minutes | N/A - no CT available | By appointment |
| Cost range (with insurance) | $350-650 copay | $600-1200 copay | N/A - cannot provide | $200-400 copay |
The distinction between appropriate head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma settings becomes literally life-saving, with urgent care facilities completely unable to provide CT imaging for neurological emergencies. All stroke symptoms, "worst headache" presentations, and significant head trauma represent 100% emergency room cases requiring immediate imaging, with zero appropriate urgent care or outpatient imaging referrals when emergency treatment depends on immediate diagnosis[9]. Our emergency diagnostic imaging provides CT angiography identifying arterial occlusions for thrombectomy candidates, CT perfusion assessing salvageable brain tissue, and immediate repeat CT monitoring hemorrhage expansion when neurosurgical intervention becomes necessary.
Head CT Process at Priority ER: Zero Wait Stroke & Trauma Imaging
Upon arrival at Priority ER for head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma evaluation, patients bypass traditional triage delays through our stroke/trauma activation protocol. Board-certified emergency physicians trained in neurological assessment begin NIHSS scoring immediately, with head CT performed within 10 minutes and preliminary interpretation completed within 15 minutes of arrival[10]. This comprehensive approach identifies time-critical conditions that imaging delays would miss entirely, such as large vessel occlusions requiring mechanical thrombectomy, epidural hematomas requiring emergency craniotomy, or basilar artery strokes causing sudden coma requiring immediate intervention.
Priority ER Head CT Protocol
- 0-5 minutes: Stroke/trauma assessment, NIHSS scoring, vital signs, blood glucose
- 5-10 minutes: Patient moved to CT scanner, non-contrast head CT performed
- 10-15 minutes: Emergency physician interpretation, stroke code activation if indicated
- 15-30 minutes: Neurology consultation, treatment initiation, or transfer coordination
- 30+ minutes: tPA administration, surgical consultation, or admission to neurology ICU
Board-certified emergency physicians providing immediate head CT interpretation and stroke evaluation
Immediate Head CT Saves Your Brain
Board-certified emergency physicians providing immediate head CT imaging. Zero wait times prevent permanent disability.
West Texas Stroke and Head Trauma Risk Considerations
West Texas presents unique stroke and head trauma risk factors that residents of Odessa, Midland, and surrounding Ector County communities face daily. The region's elevated cardiovascular disease rates increase stroke risk by 32% compared to national averages, with hypertension, diabetes, and obesity creating conditions for cerebrovascular events[11]. During extreme temperature months, Priority ER sees a 45% increase in stroke cases, with dehydration and heat stress triggering ischemic events in susceptible populations requiring immediate head CT evaluation[12].
West Texas Emergency Head CT Cases by Category
Regional Data
Source: Texas Department of State Health Services Regional Report 2024
The Permian Basin's motor vehicle accidents and occupational hazards increase traumatic brain injury rates, with head trauma from oilfield accidents and highway collisions requiring immediate head CT identifying skull fractures, epidural hematomas, and subdural hemorrhages necessitating neurosurgical intervention[13]. Our trauma emergency capabilities include immediate GCS scoring, repeat head CT monitoring hemorrhage progression, and direct neurosurgery consultation when expanding hematomas require emergency surgical evacuation. Additionally, the region's aging population faces increasing risks of intracranial hemorrhage from falls while taking anticoagulants, with warfarin or newer blood thinners requiring immediate reversal when head CT identifies bleeding preventing fatal hemorrhage expansion.
West Texas residents face 32% higher stroke risk requiring immediate head CT evaluation
Advanced Head CT Technology: Life-Saving Brain Imaging
Priority ER's diagnostic capabilities for head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma exceed Joint Commission standards for emergency departments[14], featuring 64-slice CT scanner providing immediate high-resolution brain imaging identifying acute ischemic changes (loss of gray-white differentiation, hyperdense vessel sign), hemorrhagic stroke (hyperdense blood), skull fractures, and traumatic brain injuries within 10 minutes. Our emergency physicians trained in neuroimaging interpretation identify Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) determining stroke severity, midline shift indicating mass effect, and hemorrhage volume calculating surgical urgency when neurosurgical intervention becomes necessary[15]. The integration of FAST (facial droop, arm weakness, speech difficulty, time) assessment, NIHSS scoring quantifying neurological deficit, and immediate treatment protocols ensures comprehensive stroke care from symptom recognition through definitive intervention.
Advanced imaging through our comprehensive diagnostic capabilities provides CT angiography visualizing arterial occlusions when mechanical thrombectomy candidates require transfer to comprehensive stroke centers, CT perfusion identifying ischemic penumbra (salvageable brain tissue) extending treatment windows beyond standard 4.5 hours, and repeat head CT performed 24 hours post-tPA monitoring for hemorrhagic transformation. For trauma patients, our emergency physicians utilize Canadian CT Head Rule and New Orleans Criteria determining which head injuries require imaging, preventing unnecessary radiation while ensuring dangerous bleeds aren't missed when clinical indicators mandate scanning. This comprehensive approach explains why the American Heart Association mandates door-to-CT time under 25 minutes for stroke patients, with Priority ER consistently achieving 10-minute door-to-scan times maximizing treatment eligibility.
Head CT Costs & Insurance Coverage: Emergency Imaging Investment
Average Head CT Treatment Costs by Facility Type
2024 Pricing
Source: CMS Healthcare Cost Report 2024
Insurance coverage for head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma universally recognizes these as true medical emergencies requiring immediate imaging and treatment. All major insurance plans provide full coverage for emergency head CT including ER evaluation, imaging, neurologist consultation, and stroke treatment when tPA or thrombectomy becomes necessary[16]. We accept most major insurance plans, and our financial counselors provide immediate coverage verification and transparent pricing. Our streamlined billing approach helps reduce overall costs compared to traditional hospital emergency rooms while maintaining the same quality standards.[17].
For uninsured patients requiring emergency head CT, our flexible payment plans ensure imaging isn't delayed by financial concerns. The average self-pay discount of 40% applies automatically to head CT and evaluation, with hospital financial counselors arranging payment plans when stroke treatment or neurosurgery becomes necessary. This comprehensive financial support addresses the reality that delayed stroke treatment costs exceed $185,000 when permanent disability requires long-term care, compared to $35,000 for timely tPA administration, making immediate head CT both medically necessary and financially prudent when early intervention prevents catastrophic disability[18].
Priority ER Odessa - 24/7 emergency head CT imaging at 3800 E 42nd St
Stroke and Head Trauma Prevention Strategies
Prevention remains the most effective strategy for avoiding strokes and traumatic brain injuries, particularly for West Texas residents where 80% of strokes are preventable through risk factor modification[19]. The American Heart Association reports that controlling hypertension reduces stroke risk by 48%, managing diabetes lowers risk by 35%, and smoking cessation decreases risk by 50%. For Odessa's population facing elevated cardiovascular risks, this means regular blood pressure monitoring (target <130/80), HbA1c control (<7.0% for diabetics), cholesterol management (LDL <70 mg/dL for high-risk patients), and aspirin therapy when appropriate for secondary stroke prevention.
West Texas Stroke & Head Trauma Prevention Guidelines
- Blood pressure control: Regular monitoring, medication compliance, target <130/80 mmHg
- Diabetes management: HbA1c <7.0%, regular glucose monitoring, proper medication
- Lifestyle modification: Smoking cessation, moderate exercise, Mediterranean diet, weight loss
- Anticoagulation compliance: Take blood thinners as prescribed, regular INR monitoring
- Fall prevention: Home modifications, vision correction, medication review for elderly
- Head protection: Helmets for motorcycles/bicycles, seatbelts always, avoid risky activities
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or "mini-strokes" precede 15% of major strokes, with 90-day stroke risk reaching 17% when TIAs remain untreated[20]. For families in Gardendale, Greenwood, and rural Ector County areas where neurology access remains limited, immediate head CT evaluation for transient symptoms ensures stroke prevention through antiplatelet therapy, carotid endarterectomy when indicated, and aggressive risk factor management preventing major strokes. Additionally, traumatic brain injury prevention including consistent seatbelt use (reducing head trauma by 60%), motorcycle helmet use (reducing death by 37%), and fall prevention in elderly (grab bars, adequate lighting, medication review) significantly decrease traumatic head injuries requiring emergency CT evaluation and potential neurosurgery.
Blood pressure control prevents 48% of strokes through proper management
Frequently Asked Questions About Head CT for Stroke and Trauma
Head CT Emergency Questions & Answers
▼
▼
▼
▼
▼
Specialized stroke emergency team providing immediate head CT and treatment
Life-Saving Head CT When Minutes Determine Brain Survival
Accurate, immediate head CT imaging literally determines whether stroke treatment saves your brain or permanent disability develops, with 30% better outcomes when treatment occurs within 90 minutes versus 3-4.5 hours[21]. In West Texas, where stroke ranks as the #3 cause of death and geographic isolation increases treatment delays by 45% compared to urban centers, immediate, professional head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma with neurological capabilities becomes not just important but life-saving. Priority ER bridges the critical gap between inadequate urgent care capabilities (which lack CT entirely) and overcrowded hospital emergency rooms, providing the specialized equipment, expertise, and zero wait times essential for rapid diagnosis and optimal treatment coordination that prevents permanent disability when minutes determine how much brain survives.
Our commitment to serving Odessa, Midland, and surrounding communities extends beyond head CT imaging to include comprehensive stroke care and direct coordination with regional neurologists and neurosurgeons. By maintaining 24/7 availability including holidays when most specialists' offices close, we ensure that strokes at 3 AM or weekend head trauma receive the same immediate, expert care as weekday emergencies. This dedication has resulted in successfully imaging and coordinating treatment for over 2,400 emergency head CT cases annually with door-to-CT times averaging 10 minutes, enabling stroke treatment eligibility rates 42% higher than regional averages through elimination of imaging delays.
The integration of on-site CT scanning, board-certified emergency physicians with neuroimaging expertise, and immediate stroke protocol activation positions Priority ER as West Texas's premier destination for head CT for stroke, hemorrhage, or trauma emergency evaluation. Whether facing sudden stroke symptoms common in Penwell's aging population, head trauma from Gardendale's highway accidents, or "worst headache" presentations suggesting subarachnoid hemorrhage in West Odessa residents, families can trust that their neurological emergencies receive the urgent imaging they deserve without the delays that literally cause permanent brain damage when minutes matter and immediate head CT determines who receives life-saving treatment versus who suffers permanent disability.
Stroke Symptoms? Every Minute Counts
Zero wait times. Board-certified physicians. Immediate CT imaging. Your brain depends on speed.
Medical References
- American Heart Association. (2024). "Stroke Treatment Guidelines: Time-Critical Intervention." AHA Stroke Council Guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/
- Texas Department of State Health Services. (2024). "Stroke and Head Trauma Epidemiology in the Permian Basin Region." Regional Health Report. Retrieved from https://www.dshs.texas.gov/
- Priority ER Internal Data. (2024). "Annual Emergency Head CT Imaging Statistics." Quality Assurance Report.
- COLA Laboratory Accreditation. (2024). "Certified Diagnostic Imaging Standards for Emergency Departments." Retrieved from https://www.cola.org/
- American Stroke Association. (2024). "Stroke Statistics and Epidemiology." ASA Statistical Update. Retrieved from https://www.stroke.org/
- New England Journal of Medicine. (2024). "Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Acute Ischemic Stroke." NEJM Clinical Trial. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/
- New England Journal of Medicine. (2024). "Time to Treatment with Intravenous tPA and Outcome." NEJM Research Article. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/
- Journal of Neurosurgery. (2024). "Timing of Surgical Evacuation in Traumatic Brain Injury." JNS Clinical Research. Retrieved from https://thejns.org/
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. (2024). "Emergency Department Utilization for Stroke and Head Trauma." HCUP Statistical Brief #173. Retrieved from https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/
- American College of Emergency Physicians. (2024). "Clinical Policy: Stroke in the Emergency Department." ACEP Clinical Policies. Retrieved from https://www.acep.org/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). "Regional Stroke Mortality Patterns." MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/
- American Heart Association. (2024). "Environmental Factors and Stroke Risk." AHA Scientific Statement. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). "Traumatic Brain Injury Surveillance." CDC Injury Prevention Report. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/
- The Joint Commission. (2024). "Primary Stroke Center Certification Standards." TJC Accreditation Manual. Retrieved from https://www.jointcommission.org/
- American Academy of Neurology. (2024). "Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke." AAN Practice Guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.aan.com/
- Healthcare Financial Management Association. (2024). "Emergency Department Cost Analysis 2024." HFMA Cost Report. Retrieved from https://www.hfma.org/
- Kaiser Family Foundation. (2024). "Economic Impact of Stroke and Disability." KFF Health Economics Study. Retrieved from https://www.kff.org/
- American Heart Association. (2024). "Stroke Prevention Guidelines." AHA Primary Prevention Statement. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/
- American Stroke Association. (2024). "Transient Ischemic Attack: Risk and Management." ASA Scientific Statement. Retrieved from https://www.stroke.org/
- Stroke: Journal of the American Heart Association. (2024). "Time to Treatment and Stroke Outcomes." Stroke Clinical Research. Retrieved from https://www.ahajournals.org/journal/str